So this post is a bit similar to another one I did which is called Builing a Todo List with Supabase and Nextjs. I will basically be rebuilding this in a new paid js framework called Remix Run.
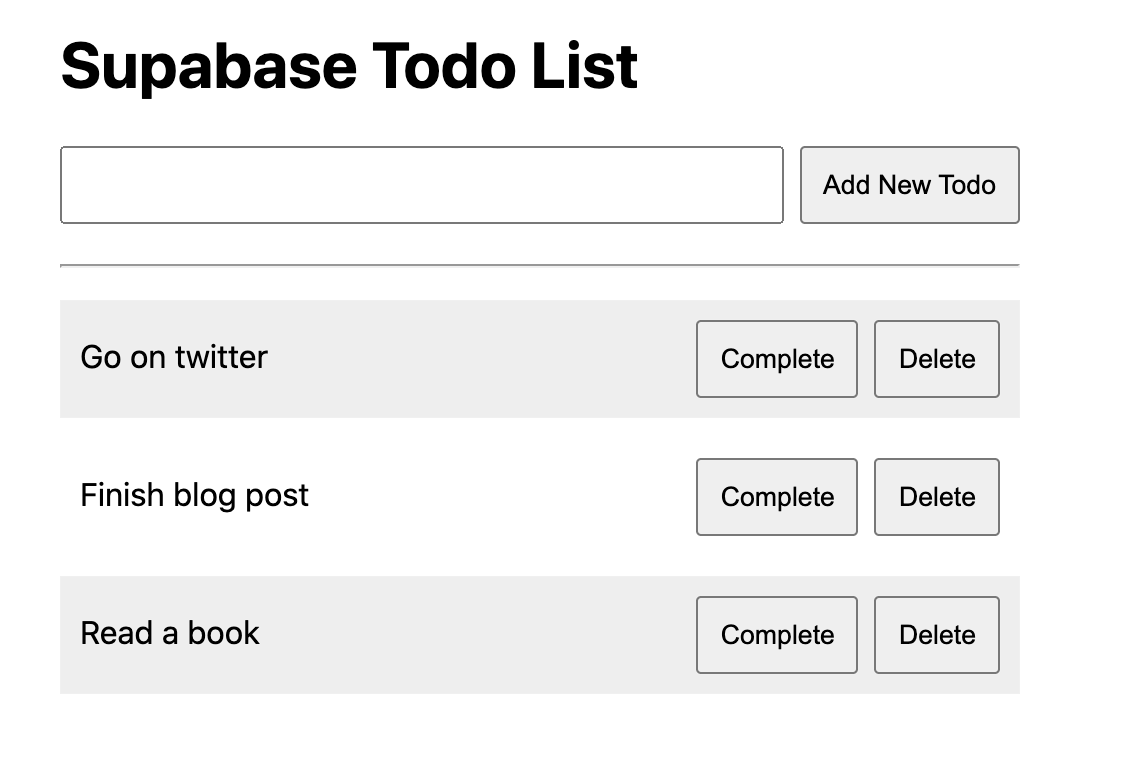
If you need a refresher of what we built last time look below.
Getting started
In order to get started with Remix you will need to run npm init remix and
follow the prompts including putting in your license key. Yes this is paid
software which is maybe a bit unusual but I think its worth it.
Setting up our env variables
Now this is something that works out of the box in nextjs but you have to do a bit of manual setup with remix.
npm install dotenv
touch .envIn your .env file have the following with your keys filled in from Supabase.
SUPABASE_URL=
SUPABASE_ANON_KEY=The next bit of configuration is to add the dotenv loader toward the top of
app/entry.server.jsx
import ReactDOMServer from "react-dom/server";
import { RemixServer } from "remix";
const dotenv = require("dotenv");
dotenv.config();Let’s also add the supabase client js library:
npm install @supabase/supabase-jsNow restart remix server which will be npm run dev
Then in an app/utils directory add a file called initSupabase.js with the
following contents.
import { createClient } from "@supabase/supabase-js";
const supabase = createClient(
process.env.SUPABASE_URL,
process.env.SUPABASE_ANON_KEY
);
export default supabase;Reading Todos
Head on over to app/routes/index.jsx where we will do the more interesting
coding.
Remix has this concept of a loader which is similar to getServerSideProps in
nextjs. To load our todos its this simple:
import { json, useRouteData } from "remix";
import supabase from "../utils/initSupabase";
export async function loader() {
const { data } = await supabase.from("todos").select("id, title, completed");
return json({
allTodos: data,
});
}Then in our component we can useRouteData and then map over our todos.
import { json, useRouteData } from "remix";
export default function Index() {
const { allTodos } = useRouteData();
return (
<ul>
{allTodos.map((todo) => (
<li key={todo.id}>
{todo.completed ? <strike>{todo.title}</strike> : todo.title}
</li>
))}
</ul>
)
}Data mutations (Create, Update, Delete)
I think this is the thing I find the coolest, but it is also a throwback to how we used to do data mutations before React.
Let’s create a Remix Form (uppercased) which is basically just a supercharged <form>
import { Form, json, useRouteData } from "remix";
<Form replace method="post">
<input type="text" name="newTodo" />
<button type="submit">Add New Todo</button>
</Form>Now this is a bit of a mental model shift. You might wonder where the onChange, and onClick is that you normally have to do with React. Well in fact forms can package this data up without individual state fields per form input. The cool thing is we could have 10 fields and they will all get serialized super easily.
It will basically do an ajax post request to this same route with all your data in it.
We can use it with an action method as follows:
import { Form, json, useRouteData, redirect } from "remix";
export async function action({ request }) {
let body = new URLSearchParams(await request.text());
if (request.method.toLowerCase() === "post") {
await supabase.from("todos").insert([{ title: body.get("newTodo") }]);
}
return redirect("/");
}To access the field value from the post request we use body.get("newTodo")
Now you can fill out the delete and complete functionality using your old school form knowledge.
<Form replace method="put">
<input type="hidden" name="completed" value={!todo.completed} />
<input type="hidden" name="id" value={todo.id} />
<button type="submit" className="complete">
Complete
</button>
</Form>
<Form replace method="delete">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value={todo.id} />
<button type="submit">Delete</button>
</Form>and then change your action to the following:
export async function action({ request }) {
let body = new URLSearchParams(await request.text());
if (request.method.toLowerCase() === "post") {
await supabase.from("todos").insert([{ title: body.get("newTodo") }]);
} else if (request.method.toLowerCase() === "put") {
await supabase
.from("todos")
.update({ completed: body.get("completed") })
.match({ id: body.get("id") });
} else if (request.method.toLowerCase() === "delete") {
await supabase
.from("todos")
.delete()
.match({ id: body.get("id") });
}
return redirect("/");
}Taking a look back at the code I had to write, this does seem a bit simpler than Nextjs.
